Learn how to consume external UPDATE (PATCH) APIs in Mendix like a
pro! In this 4th part of the Consumed API Series, we’ll walk you through how to update external data using Mendix’s built-in tools like Export Mapping, Call REST action, and dynamic headers.
Dependencies:-
You can find the published API endpoint URL below. For a better understanding of how this API was created, please refer to the previous article linked above.
Endpoint URL :- http://localhost:8082/rest/prsupdateapi/v1/UpdateApi?BookName={BookName}
JSON Structure :- {
"BookName": "string",
"Price": 0
}
headers :-
Key : Content-Type
Value : 'application/json'
First Go to MX Studio Pro & Create a non persistable entity to updating Book data dynamically with same attributes.

Go to MyFirstModule -> right click on it-> click on other->
JSON_Structue -> give the name JSON_UpdateBook.

Open JSON_UpdateBook -> Copy upper JSON & paste it here.

Go to MyFirstModule -> right click on it-> click on other -> Export_Mapping -> give the name EXP_Book.

Open EXP_Book -> Select elements & select priviously created JSON_UpdateBook , Check all & click ok.

Double click on Root entity & map with AddBook entity.


Now Create a microflow name it ACT_UpdateBook.
Go to ACT_UpdateBook
1.Take a create object activity -> Select AddBook entity & add your value.
I am adding static value you can add dynamic according to your need.

2. Create a string variable & pass the BookName for search a Book object.
Important:- We have to replaceAll white spaces with %20 Otherwise, the API request may fail or return a 400 Bad Request error.

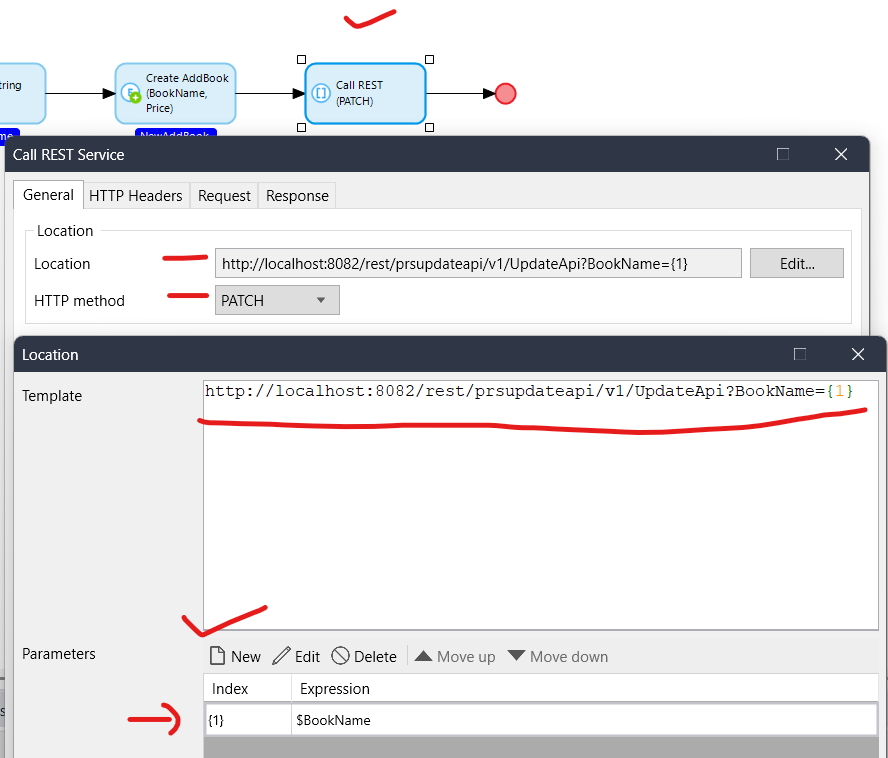
3. Take a Call REST Service activity -> Under General tab pass your endpoint URL & select HTTP method(PATCH).
Make sure to replace the {BookName} with {1} & in the parameter pass your previously created $BookName
http://localhost:8082/rest/prsupdateapi/v1/UpdateApi?BookName={1}
4. Go to HTTP Headers tab & Add above header.

5. Go to Request tab -> Select Export mapping for the entire request & map all the things.

6. Lastly, Take a Call microflow button on home page & select this microflow.

Now run the application & test it.
Important:
Since you’re using two different Mendix applications — one to publish the API and another to consume it — make sure the application where the API is published on localhost is running before making any API calls from the other app. If the publishing app isn’t running, the API request will fail.


Conclusion:
I hope this article has helped you understand How to Consume UPDATE API in Mendix.
Thanks for reading this! See you in the next blog post.

